Typically, a kidney infection develops after a UTI has already affected your bladder and urethra (the tube through which urine exits your body). This area is known as your lower urinary tract.
Whether or not you’re also experiencing kidney-specific symptoms, it’s important to look for signs of a UTI affecting your lower urinary tract:
- Painful urination (dysuria)
- Frequent urination
- Urge to go frequently, even with an empty bladder
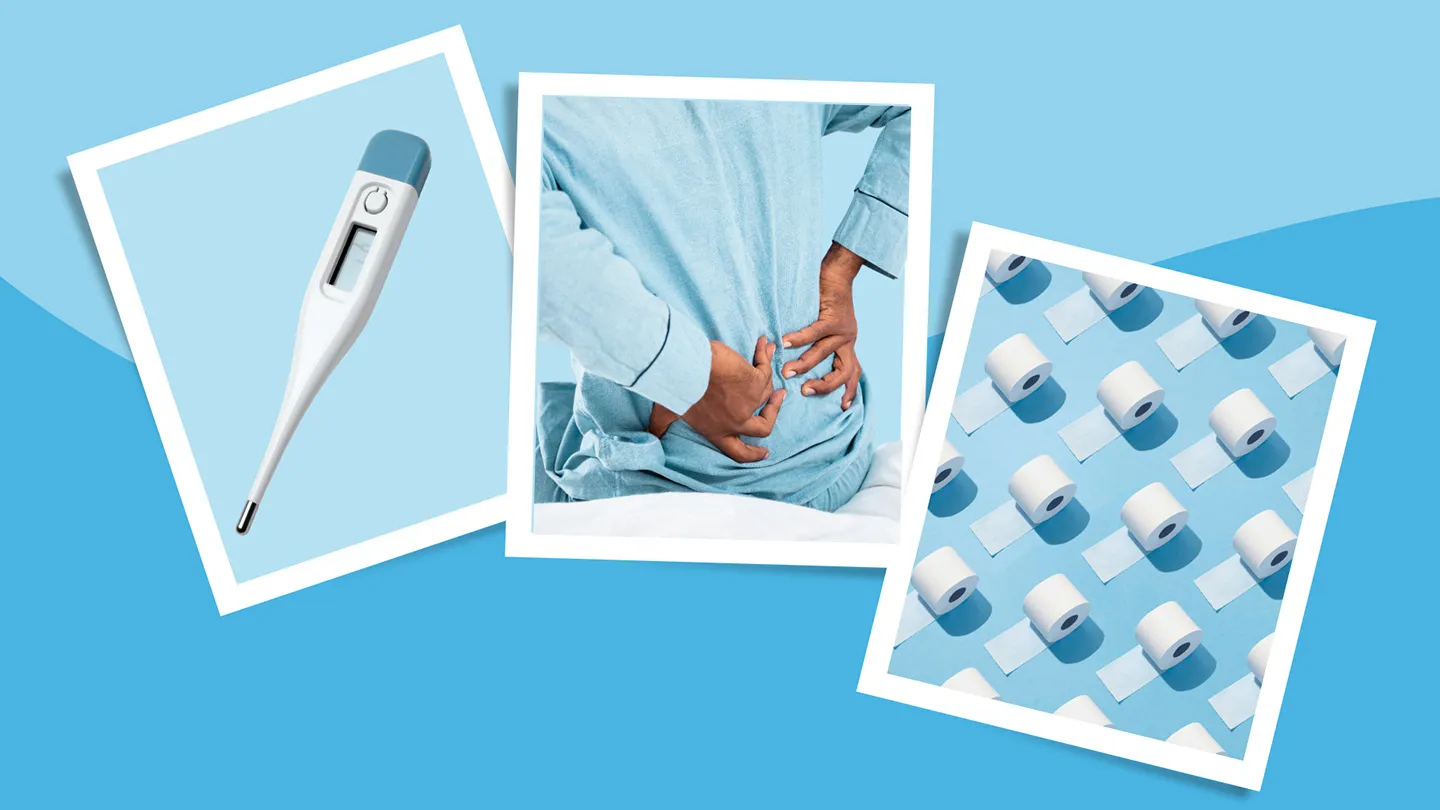
When you have a UTI that spreads to your kidneys, you’ll probably have symptoms in your lower urinary tract first. But the following symptoms indicate that your kidneys may also be affected:
- Fever and chills
- Pain in your lower back or side
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal or pelvic pain
- Cloudy or smelly urine (though this alone does not necessarily signal a kidney infection)
- Dark or bloody urine
Symptoms in Children and Elderly People
While the typical range of symptoms for a kidney infection applies to most adults, older adults and young children may have different symptoms.
Older adults may experience none of the typical symptoms of a kidney infection summarized above. Instead, they may experience cognitive symptoms. Research shows that UTIs are linked to delirium in people over 65 years old.
Children under 2 years old with a kidney infection may only have a high fever.
Caregivers of very old and very young individuals should know to seek help when these symptoms occur.
Read the full article here